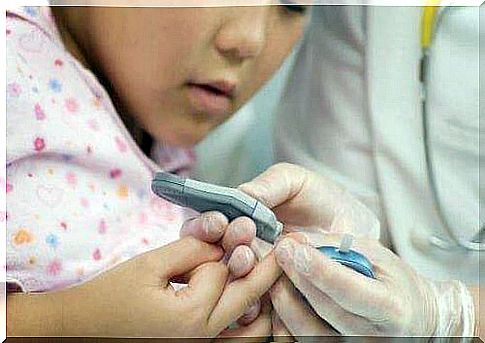
Adolescent Diabetes: Spot The Symptoms

Adolescent diabetes is a disease that continues to increase markedly from year to year. It has spread significantly around the world and, according to the World Health Organization, has increased from 5% to 10% of the world’s population.
The disease is caused when the body does not produce a sufficient amount of a hormone called insulin. Children with diabetes follow special treatment regimens to replace the necessary insulin.
The procedures associated with managing diabetes can be uncomfortable for children. Depending on their age, they must learn to give themselves insulin injections.
Children with diabetes also need to know how to test their own blood sugar levels and keep track of their carbohydrate intake with a special machine.
Managing juvenile diabetes requires constant monitoring and control. Fortunately, technological advances have improved how insulin is administered and how blood sugar levels are controlled.
This has led to better treatments and improved the quality of life for patients suffering from this disorder.
The signs of juvenile diabetes
Symptoms
In general, the symptoms of juvenile diabetes manifest themselves rapidly; they can occur over a few days or sometimes over a few weeks. Some of the symptoms may include the following:
Increased urge to urinate. Large amounts of sugar accumulate in the baby’s bloodstream, which makes the baby feel very thirsty. As a result, the child will ingest more fluids and go to the toilet more. This also makes it likely that young children with diabetes can urinate in bed.
Larger appetite. With too little insulin in circulation to help move blood sugar, it is very likely that organs and muscles are lacking sufficient energy, triggering an increased appetite.
Weight loss. One of the first symptoms of juvenile diabetes is weight loss. This disease causes greater appetite and the child eats more than usual. But without the sugar needed to produce energy, muscle tissue begins to burn the body’s fat reserves.
Fatigue or lack of energy. Since there is not enough sugar in the body, you will notice that the baby is constantly feeling tired.
Behavioral changes. Mood swings are a constant problem in children with this condition. It is very common for their moods to change frequently, from being bubbly and happy to getting angry and depressed. In addition, they may even become agitated and angry.
Breath that smells of fruit. By burning fat instead of sugar, the result is that certain substances called ketone bodies are created, causing a fruity odor of the spirit.
Blindness or blurred vision. The disease is likely to cause blindness. Having high levels of sugar in the blood can affect the crystalline fluid in the eyes.
Candidiasis. Especially in girls who have diabetes, it is very likely that they have genital fungus.
Causes of juvenile diabetes
There is no exact cause of diabetes in children, but in most cases of type 1 diabetes, it appears to be linked to the body’s immune system, which fights viruses and bacteria. In the case of type 1 diabetes, the immune system also destroys cells in the pancreas, which is what produces insulin.
Insulin is responsible for transporting sugar (glucose) around the blood to the whole body. In general, sugar enters the bloodstream by consuming food. However, when the isolates in the pancreas are destroyed, the baby produces only low levels of insulin.
The consequence is an accumulation of glucose in the bloodstream. Unfortunately, this can lead to problems that can endanger the child’s life.
Prevention
There is currently no cure or cure for type 1 diabetes. However, there have been many analyzes to determine if there is a link between children who possess certain antibodies and diabetes. However, the presence of antibodies does not mean that diabetes is inevitable.
Researchers are constantly looking for ways to prevent juvenile diabetes in children who are at high risk of suffering from this condition. In addition, other researchers are focusing on ways to avoid destruction of the isolates in the pancreas in patients who have been diagnosed.

Currently, there is nothing that can be done to reverse a diagnosis of diabetes 1 in children, but it is possible to follow a number of guidelines that can help avoid further complications:
- Help maintain good blood sugar control.
- It is important to have a healthy and balanced diet along with regular exercise.
- Visit the doctor regularly to check the condition of the child. It is recommended that children with this condition visit the doctor at least once a year and more if close monitoring is required.
It is therefore important to be aware of the symptoms in order to be able to intervene when any incidents or problems with juvenile diabetes occur.